Mission4_Potentiometer_RGB
In this project, you'll turn a potentiometer to control the LED blink rate, to make it blink faster or slower.
A potentiometer is widely used to control other devices. Unlike a button, the potentiometer provides a series of values. So it would be useful to change values within a given range, like adjusting volume, changing brightness, etc. And you will often use it in the following missions.
What you need
The parts you will need are all included in the Maker kit.
- SwiftIO board
- Shield
- Potentiometer module
- 4-pin cable
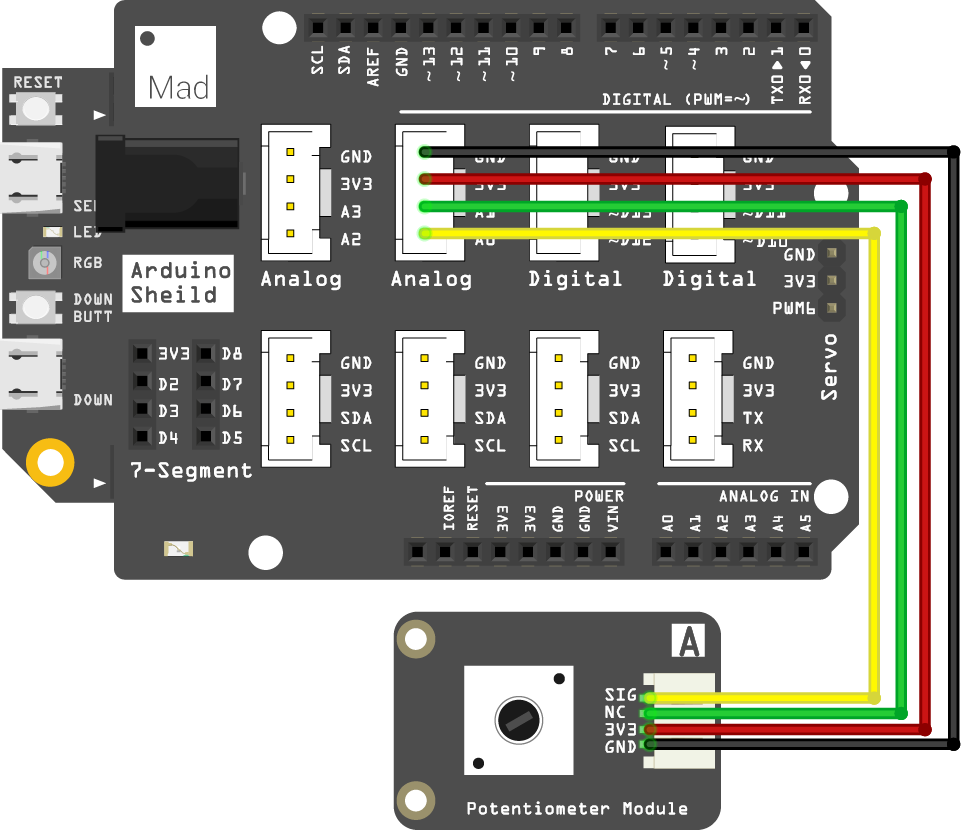
Circuit
- Plug the shield on top of your SwiftIO board.
- Connect the potentiometer module to pin A0 using a 4-pin cable.
Example code
Open the project Mission4_Potentiometer_RGB in the folder MadExamples/Examples/MakerKit if you downloaded the folder.
import SwiftIO
import MadBoard
@main
public struct Mission4_Potentiometer_RGB {
public static func main() {
let a0 = AnalogIn(Id.A0) // Initialize an AnalogIn pin A0.
let led = DigitalOut(Id.RED) // Initialize the red onboard led.
while true {
led.toggle()
// Return the percentage of the voltage in the range of 0.0 to 1.0.
let analogValue = a0.readPercentage()
let delayTime = Int(analogValue * 500)
// Stop the program for a certain period based on the value to keep current led state.
sleep(ms: delayTime)
}
}
}
Background
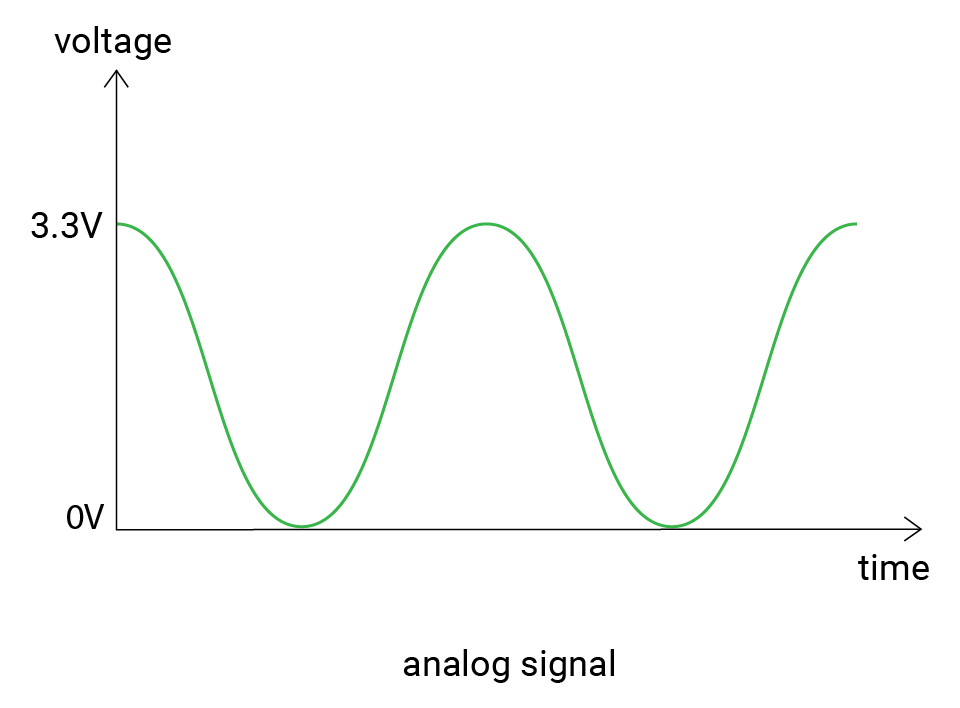
Analog signal
You have known that a digital signal has determined values. An analog signal is quite different. Its voltage changes smoothly with time. And its value ranges between 0V and 3.3V in our case. So you can get 1.5V, 2V, 2.75V... There can be infinite possible values.
So how does the board read the values? Here comes the analog to digital converter. In brief, it converts the analog voltage to a digital value that the microcontroller can read.
The converters have different precisions, called resolution, which describes the possible values they can measure. Our boards have a 12-bit resolution, which means there can be 4096 (0-4095) values in total. The values from 0 to 4095 are known as raw values.
When the board reads from the analog pin, it will first get a raw value, which will then be mapped to a voltage value proportionally. Here is the formula:
resolution / reference voltage = raw value / actual voltage
where:
resolution = 4096
reference voltage = 3.3V
For example, if the raw value equals 0, the voltage would be 0V; if the raw value equals 4095, the voltage would be 3.3V; 2047 corresponds to 1.65V.
According to the formula, you can know that the resolution will influence the precision of the final results. A higher resolution gives a result with higher accuracy.
Potentiometer
The potentiometer is one kind of variable resistor. You can adjust its resistance by rotating its shaft clockwise or anticlockwise. The internal wiper will change its position accordingly.
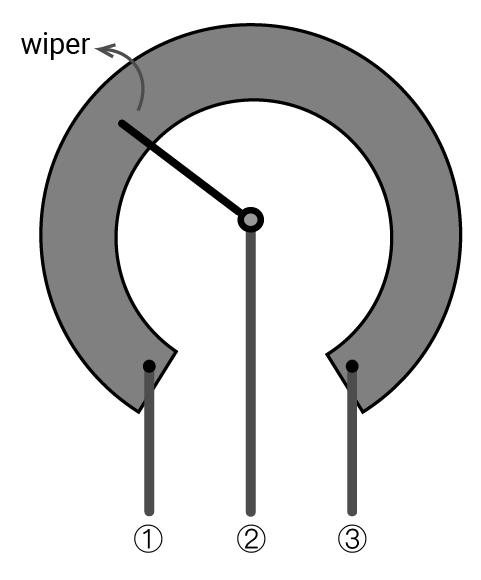
As shown above, the resistance between ① and ③ is its maximum value. The wiper divides it into two parts. As the wiper moves, the resistances of the two parts will change, which leads to voltage changes in your circuit.
Code analysis
import SwiftIO
import MadBoard
First, import the two libraries: SwiftIO and MadBoard to use everything in it. SwiftIO is used to control the input and output of the board. MadBoard defines the pin name of the board.
let a0 = AnalogIn(Id.A0)
let led = DigitalOut(Id.RED)
Initialize the red onboard LED and the analog pin (A0) that the potentiometer connects.
led.toggle()
toggle() is used to reverse the digital output voltage. If the voltage is high, it will be changed to low then, and vice versa. This statement will switch the state of the onboard LED automatically.
let analogValue = a0.readPercentage()
It allows you to get the input voltage in percentage. It represents the ratio between the raw value and the resolution (4096), so its value ranges from 0.0 to 1.0.
let delayTime = Int(analogValue * 500)
sleep(ms: delayTime)
The blink rate is decided by sleep time which is related to the input value. In this way, the potentiometer can control the LED.
Reference
DigitalOut - set whether a digital pin outputs a high or low voltage.
AnalogIn - read the value from an analog pin.
MadBoard - find the corresponding pin ids of your board.