Mission7_DC_Motors
In this mission, let's DIY a small fan. You will use a DC motor and control its speed using a potentiometer.
What you need
The parts you will need are all included in the Maker kit.
- SwiftIO board
- Shield
- Motor
- Motor driver module
- Fan blade
- Potentiometer module
- 4-pin cable
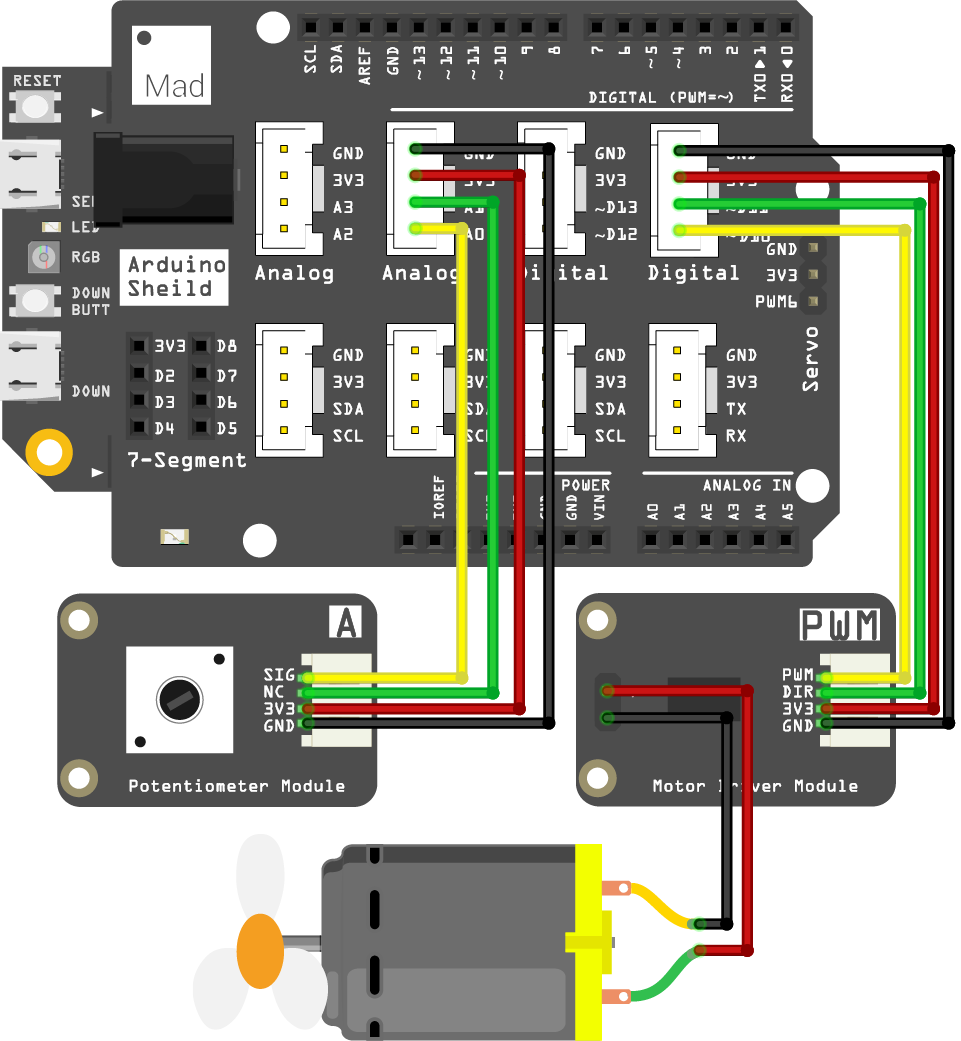
Circuit
- Plug the shield on top of your SwiftIO board.
- Connect the potentiometer module to pin A0 using a 4-pin cable.
- Connect the motor driver module to pin PWM2B (D10).
- Then connect the DC motor to the module and attach the fan blade to the shaft.
Example code
Open the project Mission7_DC_Motors in the folder MadExamples/Examples/MakerKit if you downloaded the folder.
import SwiftIO
import MadBoard
@main
public struct Mission7_DC_Motors {
public static func main() {
// Initialize the analog pin and the PWM pin
let a0 = AnalogIn(Id.A0)
let motor = PWMOut(Id.PWM2B)
while true {
// Read the input value and use it to set the duty cycle of pwm.
let value = a0.readPercentage()
motor.setDutycycle(value)
sleep(ms: 50)
}
}
}
Background
DC motor
DC motor, or Direct Current Motor, can convert electricity into motion.
It normally has two legs, a positive one and a negative one. As you connect it to the power, it will start to rotate. And if you connect the legs in an opposite direction, the motor still works but will rotate the opposite way.
Then why does it rotate when applying voltage? As the current flows, there will be an electromagnet field, and finally, cause the motor to rotate.
In this project, you will set the duty cycle to change the speed of the motor.
Code analysis
import SwiftIO
import MadBoard
First, import the two libraries: SwiftIO and MadBoard. SwiftIO is used to control the input and output of all boards. MadBoard defines the pin name of the board.
let a0 = AnalogIn(Id.A0)
let motor = PWMOut(Id.PWM2B)
Initialize the analog pin A0 for the potentiometer and the PWM pin PWM2B for the motor.
let value = a0.readPercentage()
motor.setDutycycle(value)
sleep(ms: 50)
In the dead loop, read the input value in percentage, then use this value to set the duty cycle of the PWM output. So as you rotate the potentiometer, the motor speed will change accordingly. Then set a suitable sleep time.
Ok, that's all about the code. It is quite straightforward.
Reference
PWMOut - set the PWM signal.
AnalogIn - read the voltage from an analog pin.
MadBoard - find the corresponding pin ids of your board.