Brightness control
In this example, you will use a potentiometer as a LED brightness control. As you rotate the potentiometer, the brightness changes.
What you need
- SwiftIO Micro (or SwiftIO board)
- Breadboard
- Potentiometer
- LED
- 330ohm resistor
- Jumper wires
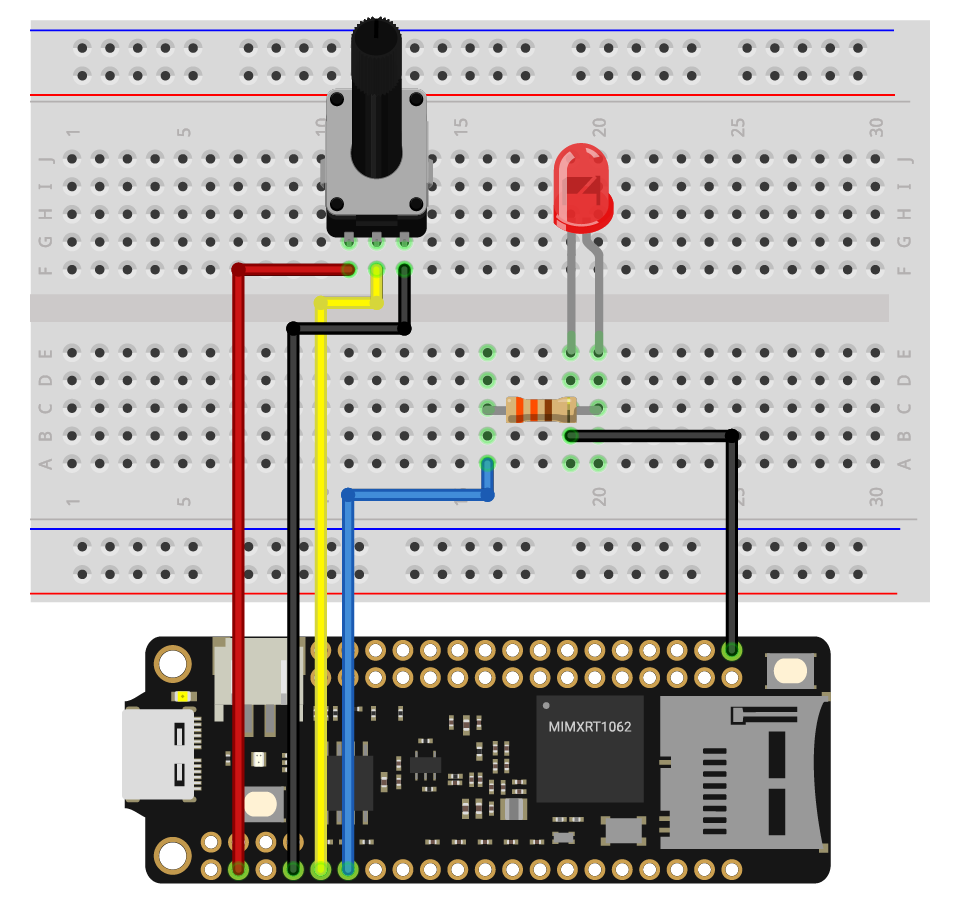
Circuit
- Place the potentiometer onto the breadboard. Connect the legs on the left to pin 3V3, connect the second leg to pin A0, and the third leg to pin GND.
- Place the LED onto the breadboard. The long leg (anode) of the LED goes to PWM0A through a resistor. The short leg (cathode) connects to GND.
Example code
Open the project BrightnessControl in the folder MadExamples/Examples/SimpleIO if you downloaded the examples.
BrightnessControl.swift
// Read the analog input value and use it to set the PWM output in order to change the LED brightness.
// Import the library to enable the relevant classes and functions.
import SwiftIO
import MadBoard
@main
public struct BrightnessControl {
public static func main() {
// Initialize an analog input and a digital output pin that the components are connected to.
let sensor = AnalogIn(Id.A0)
let led = PWMOut(Id.PWM0A)
// Allow the LED brightness control all the time.
while true {
// Read the input voltage in percentage.
let value = sensor.readPercentage()
// Light the LED by setting the duty cycle.
led.setDutycycle(value)
// Keep the current LED state for 200 milliseconds.
sleep(ms: 200)
}
}
}
Code analysis
let value = sensor.readPercentage()
There are three available methods to get analog values in different forms. In this case, you will need .readPercentage. It will return a percentage representing the ratio between actual voltage and reference voltage (3.3V). The value can then be used as duty cycle to set the LED brightness.
Reference
DigitalOut - set whether the pin outputs a high or low voltage.
AnalogIn - read the voltage from an analog pin.
MadBoard - find the corresponding pin id of your board.