PWM sound output
PWM signal can change the brightness of LEDs. You must be quite familiar with it through some projects. What's more, it allows the buzzer to generate sounds.
This example shows how to use the PWMOut to generate notes. It plays musical notes from 1 to 7 repeatedly.
What you need
- SwiftIO Micro (or SwiftIO board)
- Breadboard
- Buzzer
- Jumper wires
Circuit
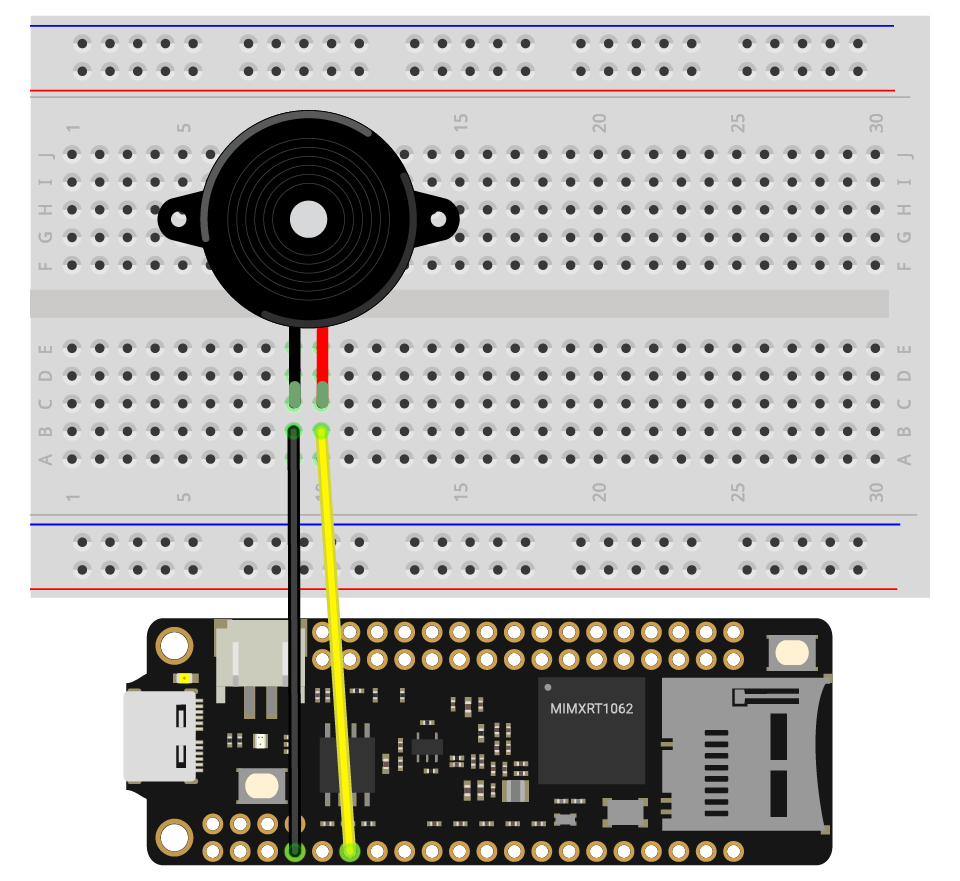
- Plug the buzzer onto the breadboard.
- Connect any one leg to the pin GND and the other to the pin PWM0A.
Example code
Open the project PWMSoundOutput in the folder MadExamples/Examples/SimpleIO if you downloaded the examples.
// Play a scale by changing the frequency of PWM signal.
// Import the library to enable the relevant classes and functions.
import SwiftIO
import MadBoard
@main
public struct PWMSoundOutput {
public static func main() {
// Initialize a PWM output pin that the speaker is connected to.
let speaker = PWMOut(Id.PWM0A)
// Specify several frequencies to produce different notes.
let frequencies = [262, 294, 330, 349, 392, 440, 494]
// Play recurrently these notes.
while true {
for f in frequencies {
// Set the frequency and the duty cycle of output to produce each note.
speaker.set(frequency: f, dutycycle: 0.5)
// Play each note for one second.
sleep(ms: 1000)
}
}
}
}
Background
Buzzer
The PWM signal outputs high and low voltage alternatively. There is a diaphragm inside the buzzer. It can move back and forth as the signal switches between on and off. The vibration causes the surrounding air to vibrate. Thus the buzzer produces the sound.
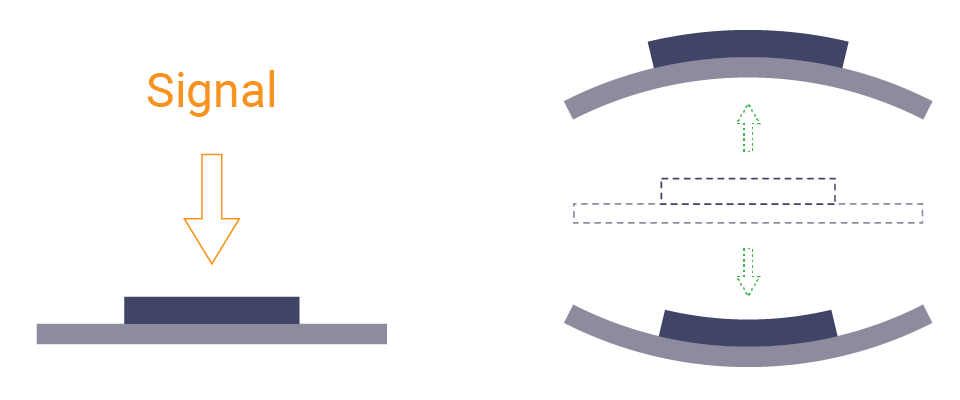
There are two kinds of buzzers.
- An active buzzer has an internal circuit to create alternating voltage. So you can connect it to power.
- A passive buzzer needs a PWM signal to vibrate the diaphragm. The frequency will influence the pitch. A higher frequency will produce a higher pitch.
Code analysis
let frequencies = [262, 294, 330, 349, 392, 440, 494]
This array stores the frequencies of seven notes from 1 to 7. The first frequency corresponds to middle C.
speaker.set(frequency: f, dutycycle: 0.5)
The frequency is an essential factor for sound pitch. The method set(frequency:dutycycle:) allows you to set both the frequency and duty cycle of a PWM signal. So here you will use the frequencies in the array to set the signal.
sleep(ms: 1000)
This statement defines the duration of notes. Each note will last one second.
Reference
PWMOut - set the PWM signal.
MadBoard - find the corresponding pin id of your board.