Introduction to microcontroller
In brief, the MadMachine project focuses on the combination of microcontroller and Swift language. You can program hardware in Swift language to build interactive projects. In this tutorial, let's dive into microcontrollers and learn how it works.
Overview
What is a so-called microcontroller (MCU)? It is usually embedded in all kinds of electronic devices, like home appliances and serves as the heart of these devices to execute some specified tasks. It can take input from the physical world (sensors) and control output devices (actuators).
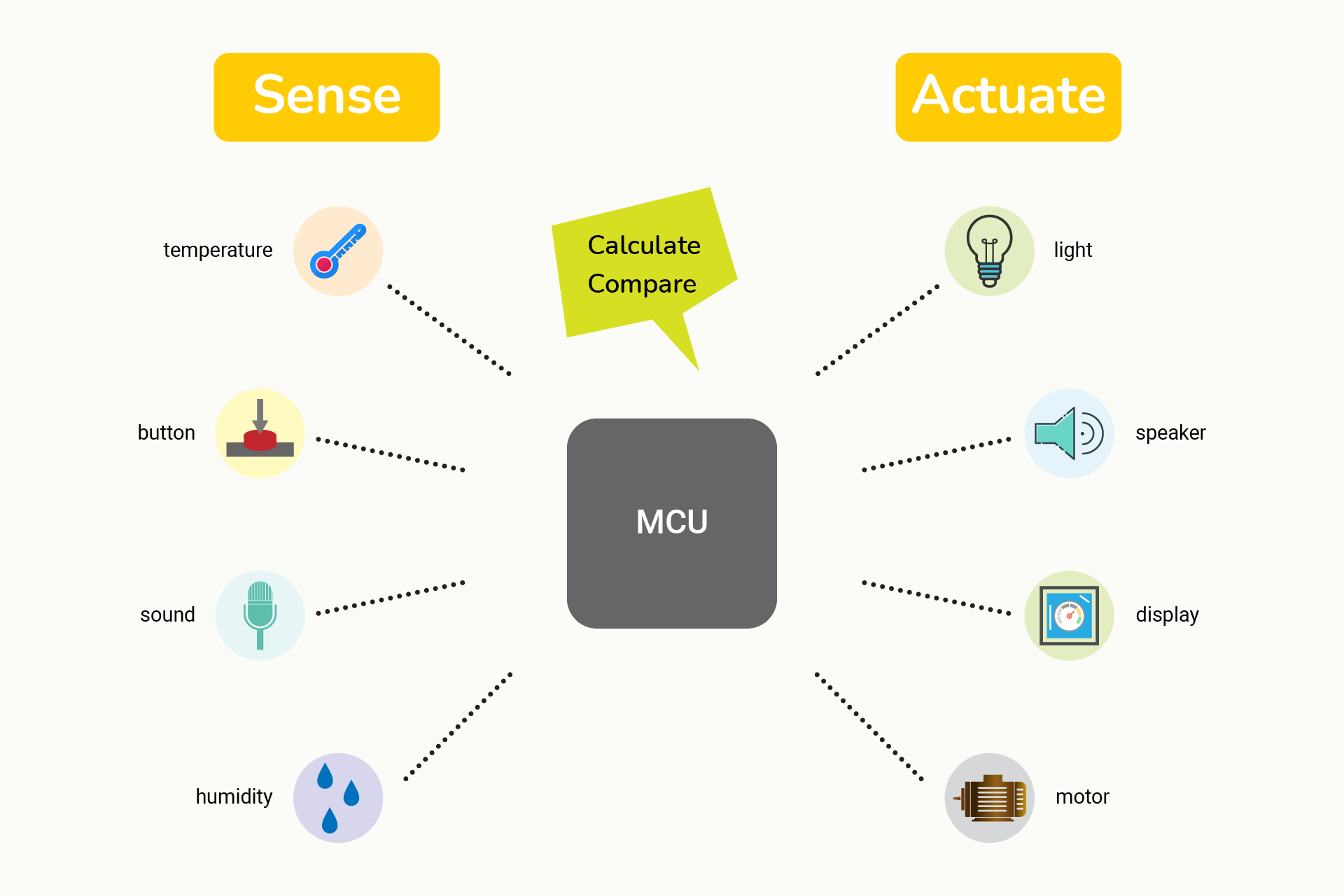
When you use your computer, you type text with a keyboard. In this case, the keyboard serves as an input device; the screen will display the result and thus is an output device. Now come back to MCU. It can work with various devices. Suppose that you connect it to a switch and a light: the switch serves as an input to detect your action and the LED as an output to generate light. There are tons of devices with different usage, so an MCU can do different tasks after connecting to all kinds of devices.
How it works
It's quite like how humans sense and react to the environment.
Humans sense the environment through their five senses: sight, hearing, taste, touch, and smell. These senses collect information about the environment and send it to the brain for processing. The brain then interprets this information and generates a response.
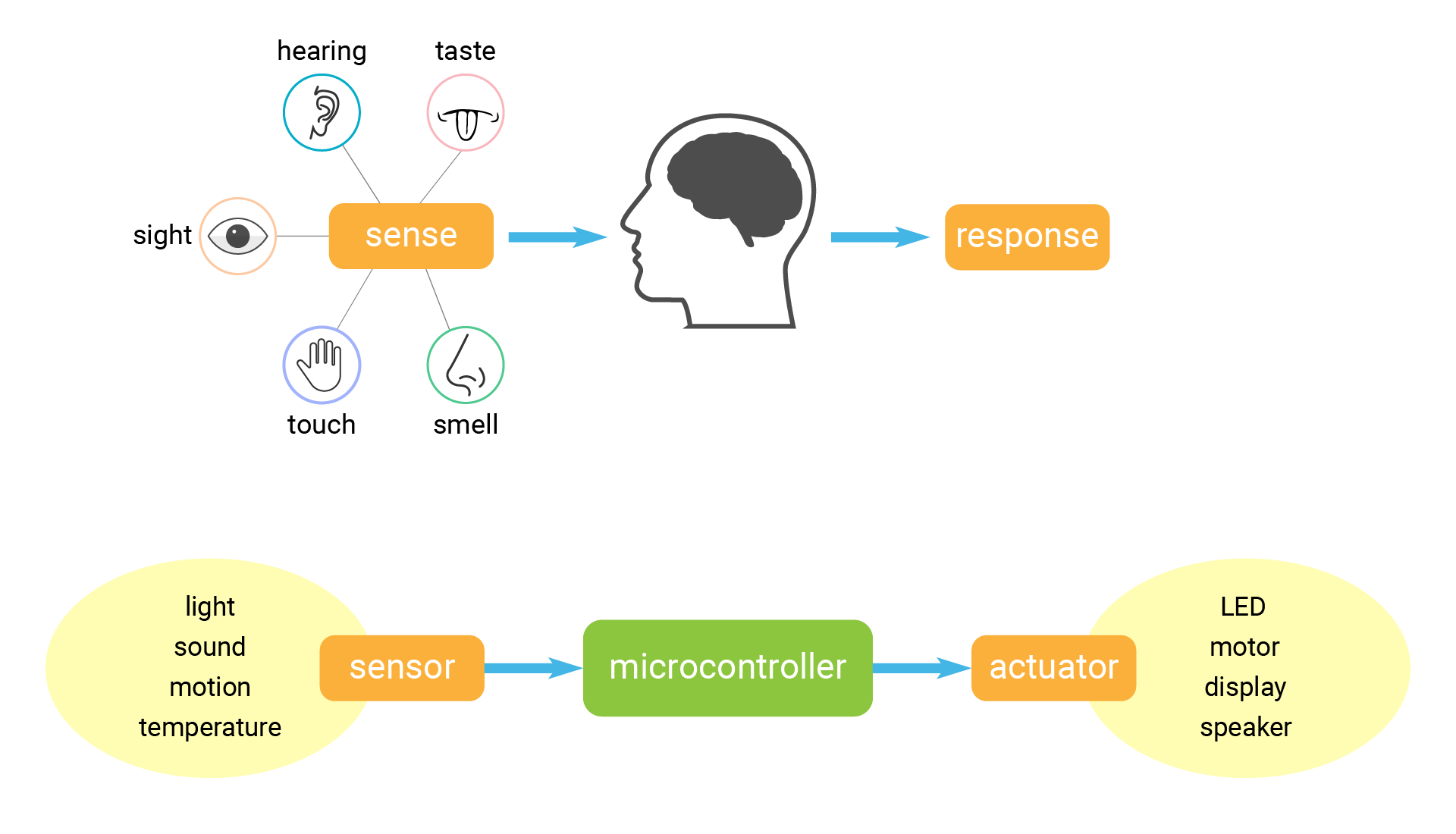
Similarly, MCU reads input signals from external devices/sensors through its I/O ports and processes the data using its internal processing capabilities. Then MCU controls various types of devices according to its logic, such as LEDs, displays, and motors...
What it consists of
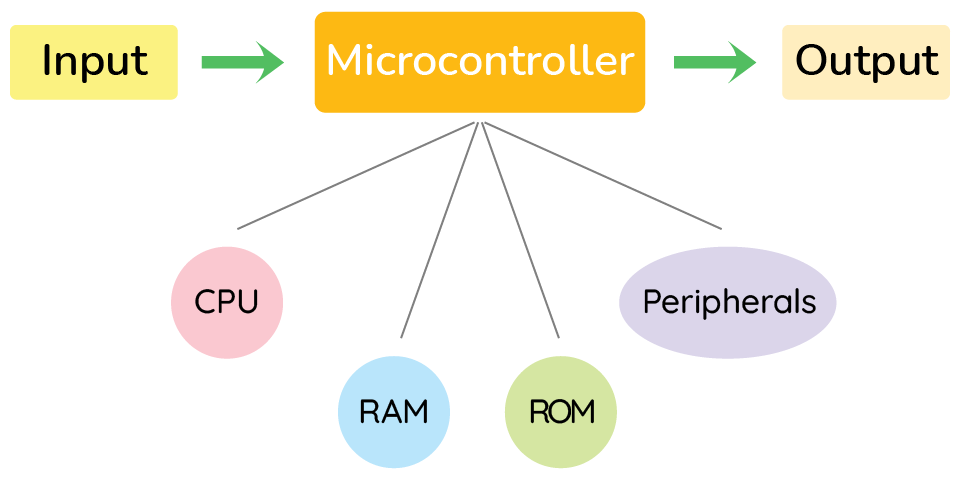
An MCU usually contains a CPU, RAM, ROM (can be understood as RAM that can only be read from but cannot be changed), and different kinds of I/O peripherals in a single chip, to interact with external devices. Other devices will be attached to its pins to allow it to sense and react to the physical world.
MCU vs General-purpose Computer
I believe most of you guys are software programmers, so it would be a good practice to compare MCUs to general-purpose computers you use in everyday life for a better understanding.
| Component | MCU | General-purpose computer |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | executes a specific set of instructions normally optimized for low power consumption. The core speed is around 8Mhz to hundreds of Mhz. | executes more complex instructions. The core speed is around 2 - 4GHz, and multiple cores are common. |
| RAM | is about 128K-2MB. | has much larger size, 2GB-32GB, fast access time. |
| ROM | stores the application which is called firmware. | stores the BIOS to initialize all the devices, including hard disks. |
| Peripherals | GPIO, I2C, SPI, UART... All peripherals, as well as CPU, ROM, RAM, are integrated into a single chip. | USB, Ethernet, SATA... All peripherals, as well as CPU, ROM, RAM, are connected to the motherboard and communicate through buses on it. |
| External storage | SD card | hard disk |
| Usages | is embedded in devices and runs a specific task continuously without interruption | runs multiple applications simultaneously. |
| Programming | involves low-level programming and a deep understanding of the underlying hardware. | focuses on writing high-level software applications** without needing to know the details of the underlying hardware. |
Major difference
MCUs and general-purpose computers have many notable differences, such as clock speed, memory size, cost, usage, power consumption... You can find many articles online that explain these differences in detail.
However, the most important difference actually lies in MMU (memory management unit) which is discussed in this blog.
MMU is a hardware component in a computer to manage access to memory by mapping virtual memory addresses to physical memory addresses. It helps the operating system to run multiple processes simultaneously by isolating their virtual address spaces. MCUs run a single application and all code use directly the physical memory addresses.
MCUs were originally designed for simple, self-contained devices. However, with the latest advancements in technology, MCUs have become more powerful and capable of handling more complex tasks. The increased processing power and memory capacity of modern MCUs, combined with the availability of high-level programming languages, is making it possible to build sophisticated applications that were previously not possible.
There are many popular microcontroller boards like Arduino, MicroPython... Each one uses a different language and has its advantages. And our boards (SwiftIO Micro or SwiftIO board) use the Swift language.
On the other hand, Raspberry Pi runs a full Linux operating system and can be regarded as a well-equipped computer. So when you program for the Raspberry Pi, you are essentially programming applications that run on Linux.