Morse code
You have used an LED to generate an SOS signal and know a little about morse code in previous tutorial. Now you will learn more about it and type messages with it.
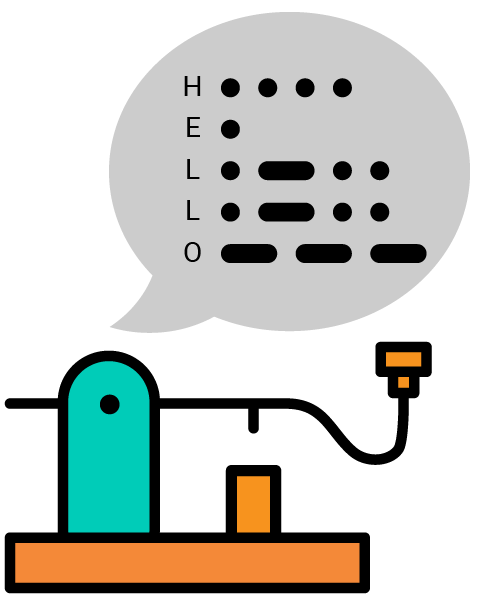
Background
As mentioned before, morse code uses a sequence of dits and dahs (dots and dashes) to represent characters. The duration of the dah is three times the duration of the dit. Here is the chart of morse code.

There are also some requirements for the gap between each code:
- The gap between morse codes (dits and dahs) within a character equals a dit duration.
- The gap between letters equals 3 dit duration.
- And the gap between words equals 7 dit duration.
In this project, you will send morse code using a button. A long button press represents the dah, and a short press represents the dit.
Circuit
You will use a button (D1) as an input and an LCD (SPI0) for text display. The button (D1) and the LED (D18) are used for notifications.
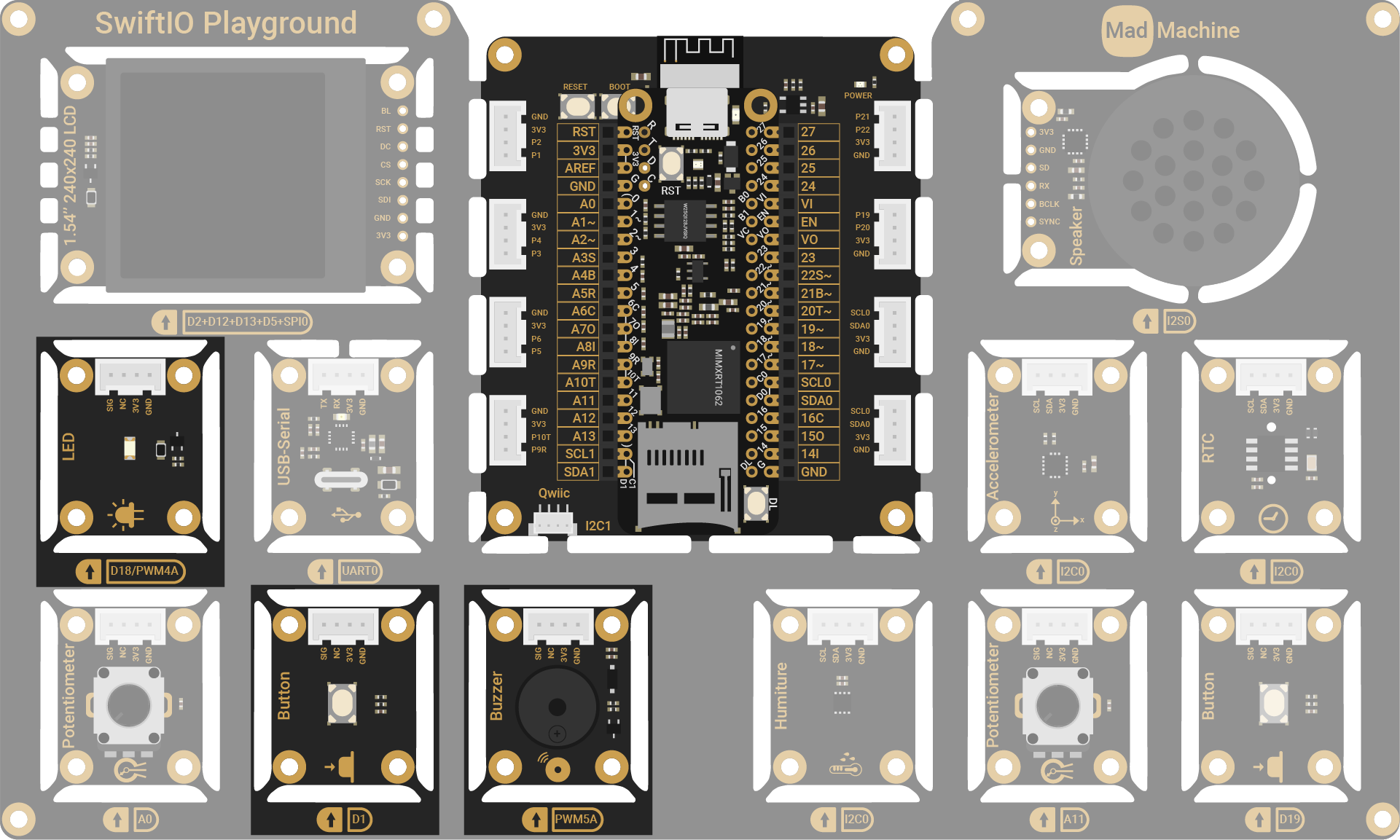
Project overview
- Read digital values from the button.
- Once it's true, the button is pressed. Check how long the button is pressed.
- If the button press is longer than 300ms, the morse code is a dah, or else it's a dit.
- Once the button is released, store the time after it.
- The threshold for the gap between words is 150ms, and the gap between letters is 60ms. The sound from the buzzer serves as a notification.
- If the morse code for a letter is done, find the corresponding letters and print it.
- Repeat the process until a word is finished. Add a space after the word.
As you can see, the key point of this program is the state of the button. If it's pressed, you need to know if it's a long press or a short press. If it's released, you need to store the gap before the next press to tell if it's the gap between letters or words.
Example code
You can download the project source code here.
// Import the SwiftIO library to set input/output and MadBoard to use pin id.
import SwiftIO
import MadBoard
@main
public struct MorseCode {
public static func main() {
// Initialize an LED as an indicator.
let led = DigitalOut(Id.D18)
// Initialize a button used to type characters.
let button = DigitalIn(Id.D1)
// Initialize a buzzer used to tell typing states.
let buzzer = PWMOut(Id.PWM5A)
// Create a periodic timer that alerts every 10s.
let timer = Timer(period: 10)
// Store the morse code for 26 letters and 0-9.
let dict: [String: String] = [
".-": "A", "-...": "B", "-.-.": "C", "-..": "D", ".": "E",
"..-.": "F", "--.": "G", "....": "H", "..": "I", ".---": "J",
"-.-": "K", ".-..": "L", "--": "M", "-.": "N", "---": "O",
".--.": "P", "--.-": "Q", ".-.": "R", "...": "S", "-": "T",
"..-": "U", "...-": "V", ".--": "W", "-..-": "X", "-.--": "Y",
"--..": "Z",
".----": "1", "..---": "2", "...--": "3", "....-": "4", ".....": "5",
"-....": "6", "--...": "7", "---..": "8", "----.": "9", "-----": "0"
]
// Each morse code consists of a sequence of dits and dahs.
let dit = "."
let dah = "-"
// Store the input morse code for a character.
var morseCode = ""
// Store all characters.
var text = ""
// A threshold for a long press which matches a dah.
let longPressCount = 30
// Thresholds to decide if you have finished type a character or a word.
let letterReleaseCount = 60
let wordReleaseCount = 150
// Store the duration of a specified button state to compare with the thresholds above.
var pressCount = 0
var releaseCount = 1
// Store the states of the button.
var justPressed = false
var justReleased = false
var buzzerCount = 0
var lastLetter = ""
timer.setInterrupt() {
if button.read() {
// If button is pressed, store the duration to judge if it's long press or short press.
// The LED will be on as an indicator.
if pressCount == 0 {
justPressed = true
}
pressCount += 1
led.write(true)
} else {
// If the button is not pressed, store the duration to judge if
// you have finished typing a character or a word.
// Turn off the LED.
// If you haven't pressed the button after downloading your project,
// releaseCount also increases. So the variable justReleased is used to
// check if the button is pressed and then release.
if releaseCount == 0 {
justReleased = true
}
releaseCount += 1
led.write(false)
}
// Mute the buzzer after a specified period.
buzzerCount += 1
if buzzerCount > 10 {
buzzer.suspend()
}
}
while true {
// Check if you finish typing a single character or a word.
if releaseCount > wordReleaseCount {
// If the time after the button is releases exceeds the threshold,
// add a space after what you have typed.
// The buzzer produces a higher sound as a notification.
if lastLetter != "" && lastLetter != " "{
text += " "
print("Message: \"\(text)\"")
buzzer.set(frequency: 2000, dutycycle: 0.5)
buzzerCount = 0
lastLetter = " "
}
morseCode = ""
} else if releaseCount > letterReleaseCount {
// Check if the morse code matches a character.
// If so, display it on the LCD and make the buzzer to produce a sound.
if let letter = dict[morseCode] {
text += letter
print("Message: \"\(text)\"")
lastLetter = letter
morseCode = ""
buzzer.set(frequency: 1200, dutycycle: 0.5)
buzzerCount = 0
}
}
// Right after you release the button, get the morse code based on the time that the button is pressed and store it.
if justReleased {
if pressCount > longPressCount {
morseCode += dah
} else {
morseCode += dit
}
justReleased = false
pressCount = 0
}
// Check if you have press the buuton. If so, it will get ready to store the duration after the button is release.
if justPressed {
justPressed = false
releaseCount = 0
}
sleep(ms: 1)
}
}
}